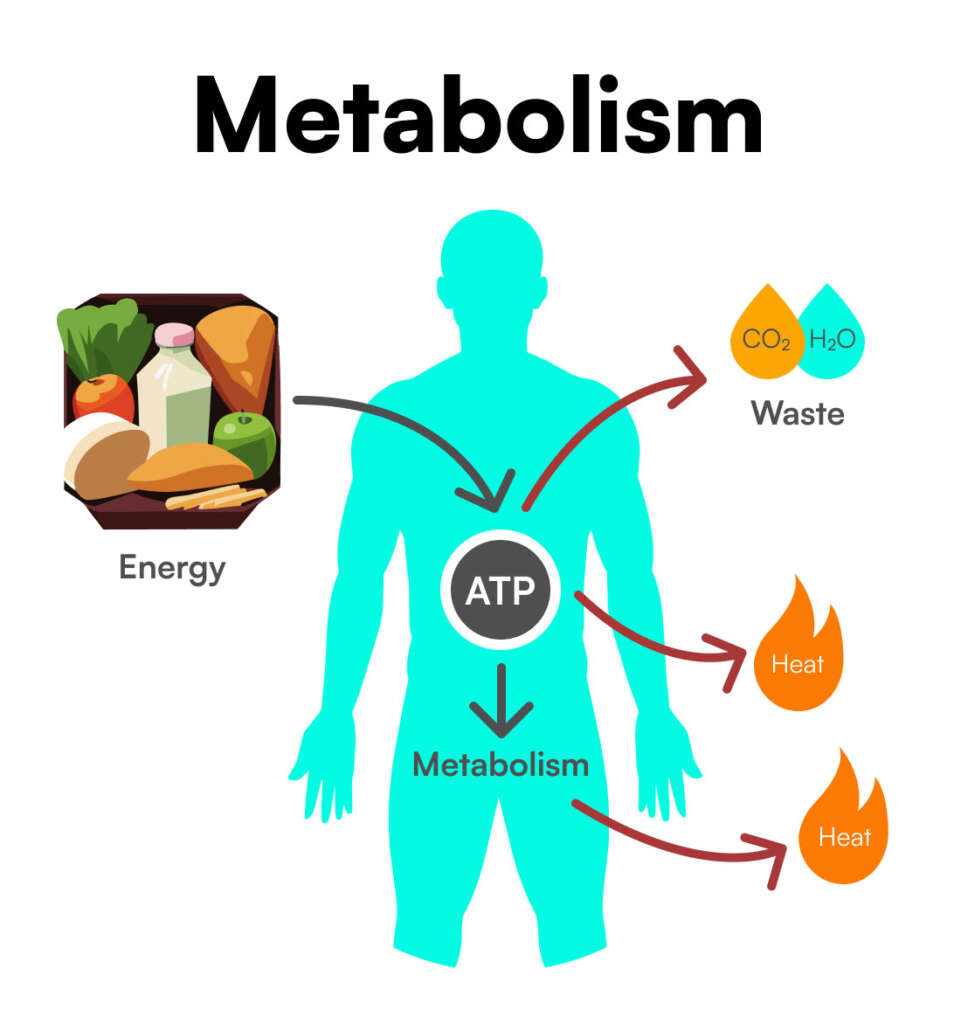
Metabolism is the complex chemical processes that occur in your body. These processes involve the conversion of food and drink into energy and building blocks for proteins, lipids, nucleic acids (like adenosine triphosphate – ATP), and some carbohydrates, as well as the elimination of nitrogenous waste. This conversion process is very important because it enables cells to perform their necessary functions, like growth, repair, and response to their environments.
Metabolism and calories
Calories are a measure of energy, and they come from the food and beverages we consume. Metabolism converts these calories into energy you need to power everything you do, from moving to growing, even thinking. The metabolic rate determines how many calories you burn over a period of time – i.e. how fast your body burns calories. There are several components to this:
- Basal metabolic rate (BMR): This is the amount of energy your body needs to maintain basic physiological functions when it’s resting. This means mostly functions like breathing, circulating blood, and cell production. BMR accounts for 60-70% of the energy your body utilizes.
- Thermic effect of food (TEF): This refers to the energy used to digest, absorb, and metabolize food nutrients.
- Physical activity: This includes all activities from daily tasks to structured exercise. It’s the most variable component of energy expenditure.
What influences metabolism
There are many factors that influence metabolism. Understanding these factors can help you make more informed decisions about your diet and exercise to influence your metabolic rate and overall energy balance.
- Age: when you are getting older your muscle mass tends to reduce, you have more fat, and you experience hormonal and neurological changes.
- Sex: Generally, men have a faster metabolism than women because they have more muscle mass, heavier bones, and less body fat.
- Body composition: People with more muscle mass have a higher metabolic rate because muscle tissue burns more calories than fat tissue, even at rest.
- Size: Larger bodies have a higher metabolic rate because they have more cells and require more energy to maintain their basic functions.
- Genetics: Genetic factors can also be determining.
- Physical activity: The more active you are, the more calories you burn. Regular exercise increases muscle mass, which boosts your metabolic rate.
- Hormones: Thyroid hormones play a significant role in regulating metabolism. Conditions like hypothyroidism can slow metabolism, while hyperthyroidism can accelerate it.
- Diet: Caffeine and spicy foods can temporarily speed up metabolism
- Temperature: Being in a very cold or very hot environment can increase your metabolic rate as your body works harder to maintain a normal temperature.
Does metabolism affect weight?
Yes, metabolism significantly affects weight. Weight management is basically about energy balance, which means balancing the energy (calories) you take in through food and drinks with the energy your body uses for all the things we mentioned earlier. If you consume more calories than you burn, you’ll gain weight; if you consume fewer calories than you burn, you’ll lose weight. But don’t forget that there are other factors that play a role in metabolism – as described in the previous part.
Common misconceptions about metabolism
Fast metabolism means thin body
Faster metabolic rate doesn’t automatically guarantee thinness. It can contribute to burning more calories, but it’s more complicated. Body weight and composition are influenced by other factors including diet, physical activity, genetics, hormonal balance, and overall lifestyle and health.
Menstrual cycle affects metabolism
There’s a common belief that the menstrual cycle influences metabolism. While the topic is being studied, there is still not enough scientific evidence to provide a definite answer. For now, it looks like some women’s metabolism can be slightly different around their cycle, while others don’t experience a significant difference.
Green tea helps with weight loss
Another popular belief is that green tea, thanks to its caffeine and antioxidants, can help you lose weight. Green tea can indeed be healthy for you but to lose weight, you need to consume extracts or EGCG supplements that are much more concentrated than the beverage. And even in that case, the effects are quite modest.
Wrapping up
Metabolism converts your food and drink into energy to enable cells to grow and repair. The most of the energy is used for the basic physiological functions, like breathing, circulating blood, and cell production. Metabolism is a very complex system of processes influenced by many factors from age to size to diet, and so on and so forth.
Sources:


